What Is The Effect Of A Monetary Contraction In A Fixed Exchange Rate System?
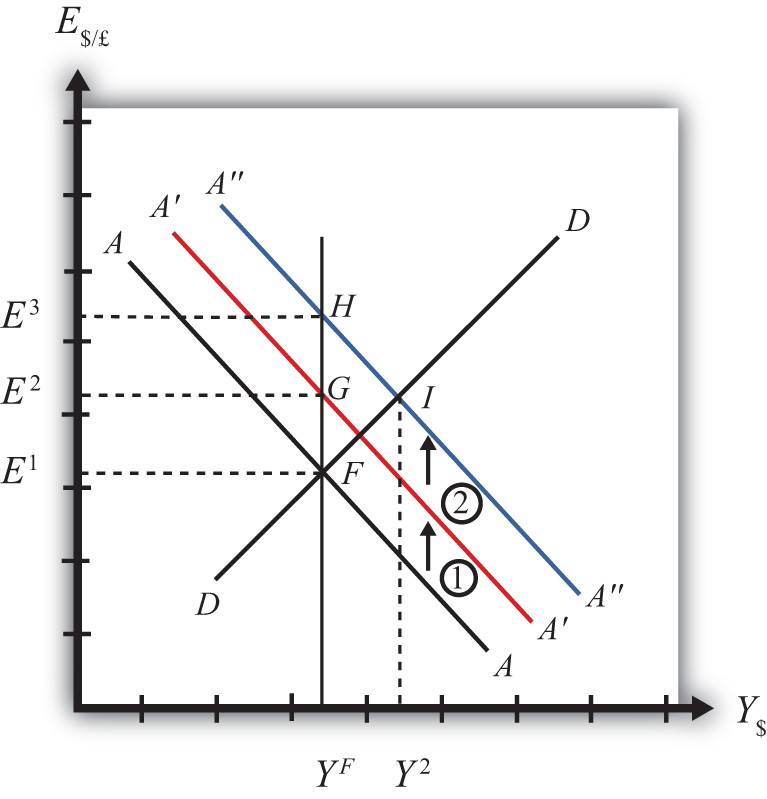
What is the effect of a monetary contraction in a fixed exchange rate system?. US contractionary monetary policy will cause a reduction in GNP a reduction in the exchange rate E implying an appreciation of the US dollar and a decrease in the current account balance. In plain English we can say as follows. Therefore a monetary contraction in a foreign country should be accompanied by a domestic monetary contraction to maintain the exchange rate fixed.
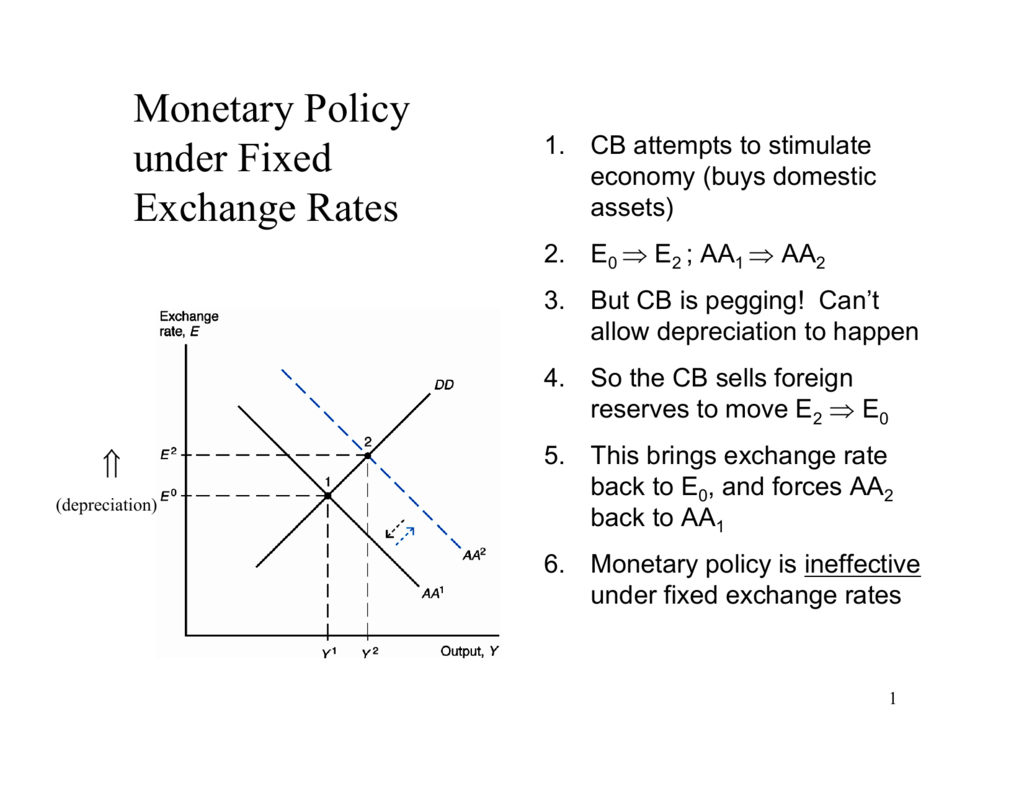
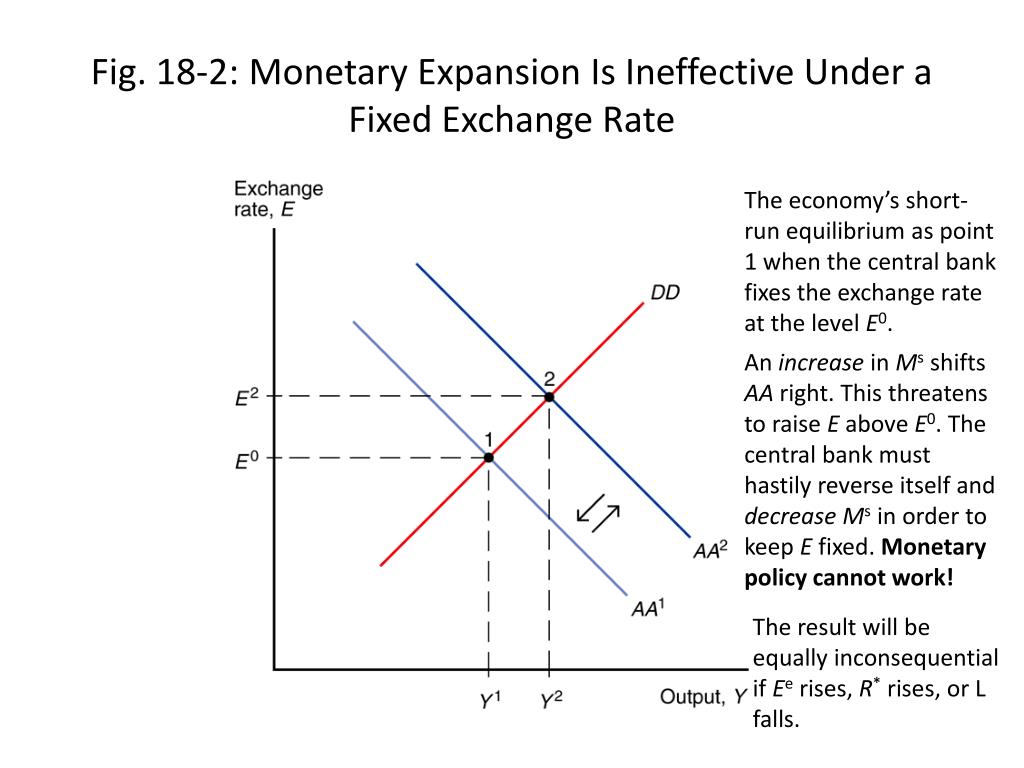
When the exchange rate is fixed money supply must be used to keep the exchange rate stable so the government cannot determine money supply freely In other words a fixed exchange rate ties the hands of the monetary authority. These results suggest that in the short run the monetary accomodation effect under a fixed exchange rate outweighs the leakage effect following from a large degree of openness to trade. The currency essentially wont buy as much as it would before.
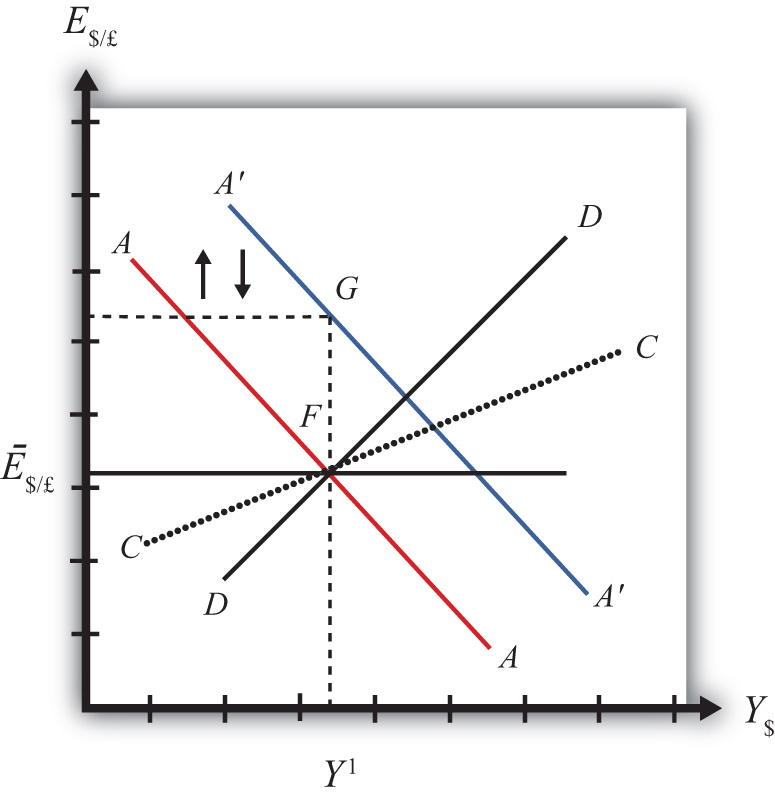
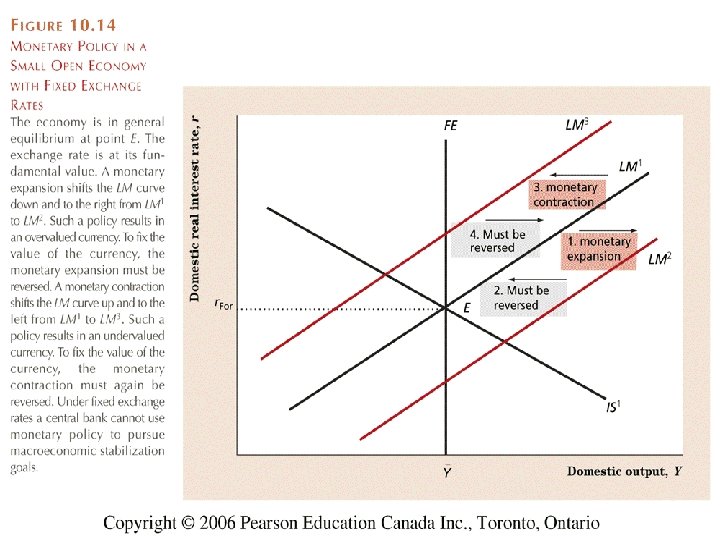
Effects of contractionary monetary policy. The fixed exchange rate regime demands strict monetary discipline by the government. This is shown in Fig.
When this happens prices rise and the currency within the economy is worth less than it was before. The quick effects however are as follows. Inflation occurs when an economy grows due to increased spending.
When a currency is worth less its exchange rates. B It increases the demand for money. This however cannot be allowed.
70 What is the effect of a monetary contraction in a fixed exchange rate system. There is also the possibility of uncertainty in relation to the maintenance of the fixed exchange rate regime. It increases the demand for money.
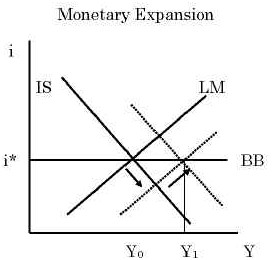
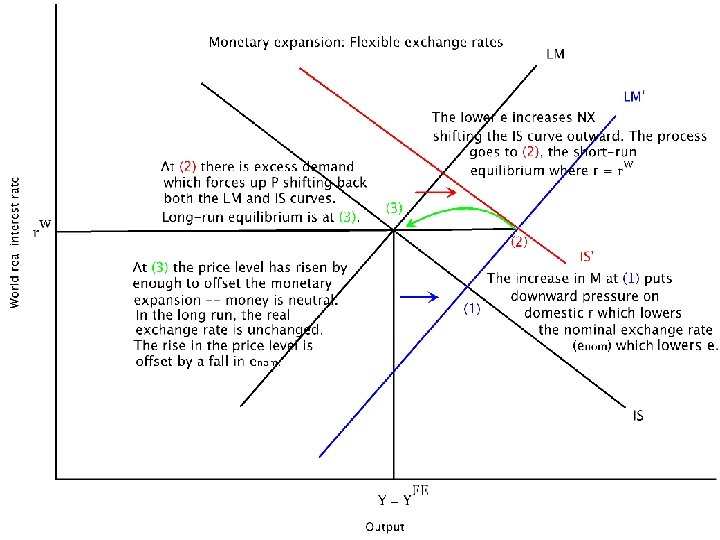
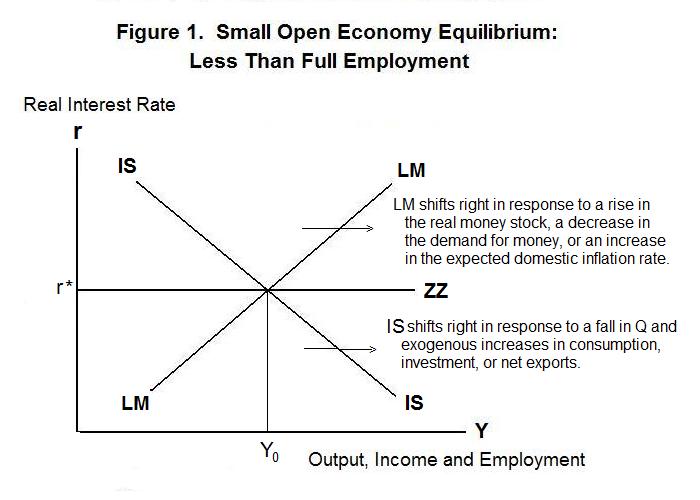
A monetary contraction tends to increase the interest rate decreasing investment and lowering equilibrium output. The policy trilemma shows that monetary policy autonomy is more constrained under fixed exchange rates than under flexible exchange rates.
US contractionary monetary policy with a fixed exchange rate will have NO EFFECTS within the economy.
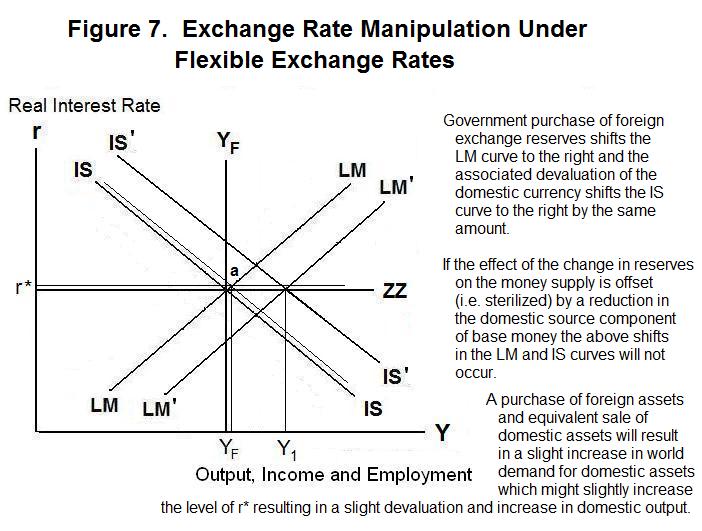
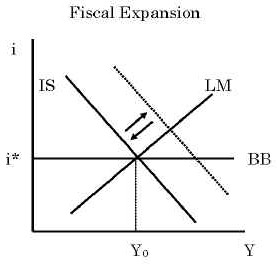
Monetary policy in a fixed exchange rate system is equivalent in its effects to sterilized Forex interventions in a floating exchange rate. There are no effects from expansionary or contractionary monetary policy in a fixed exchange rate system. There is also the possibility of uncertainty in relation to the maintenance of the fixed exchange rate regime. Explain how expansionary and contractionary monetary policies affect aggregate demand through the exchange rate channel. In plain English we can say as follows. The fixed exchange rate regime demands strict monetary discipline by the government. Contraction in Money Supply under Fixed Exchange Rate System. These results suggest that in the short run the monetary accomodation effect under a fixed exchange rate outweighs the leakage effect following from a large degree of openness to trade. The exchange rate will not change there will be no effect on equilibrium GNP and there will be no effect on the current account balance.
The policy trilemma shows that monetary policy autonomy is more constrained under fixed exchange rates than under flexible exchange rates. Multiple Choice Skipped It leads to an inflow of money from abroad It puts downward pressure on a fixed exchange rate. An implication of this is that inflation should be more tempered in a fixed exchange rate regime than in a flexible exchange rate regime because of the effects of the maintenance of the peg on monetary policy discipline and the. Therefore a monetary contraction in a foreign country should be accompanied by a domestic monetary contraction to maintain the exchange rate fixed. If the central bank decreases money supply domestic interest rates increase and output decreases. The exchange rate will not change there will be no effect on equilibrium GNP and there will be no effect on the current account balance. A It forecasts low Version 1 47.


























Post a Comment for "What Is The Effect Of A Monetary Contraction In A Fixed Exchange Rate System?"